Molecular Probes
The Manetsch laboratory maintains a strong interest in the development of molecular probes that upon refinement can serve as tools for fluorescence or mass spectrometry-based study of biologically relevant molecules or processes. We propose that specific labeling tools will facilitate and accelerate the discovery of potential biomarkers or drug targets within complex systems. The Manetsch laboratory is also interested in the development and application of labeling and tagging moieties enabling the enrichment of the labeled biomolecules from the non-labeled ones.
Cyclic Thiosulfinates

As part of an ongoing collaboration with the laboratory of Dr. Jeffrey N. Agar, our group maintains an interest in the synthesis and cross-linking evaluation of known and novel cyclic thiosulfinates. This work addresses the need for chemical tools that can selectively and reliably form cross-links with proximal thiol pairs present in protein targets associated with various aggregate diseases. We have demonstrated in a recent publication that the thiol pair Cys111A and Cys111B of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1), present in ALS can be cross-linked by cyclic thiosulfinates while avoiding toxic “dead-end” modification of lone thiols. These pioneering efforts led to the synthesis and cross-linking evaluation of 5- to 7-member ring cyclic thiosulfinates which functioned in the presence of biological concentrations of glutathione and acted as cell-permeable, potent, tolerable, intracellular cross-linkers.
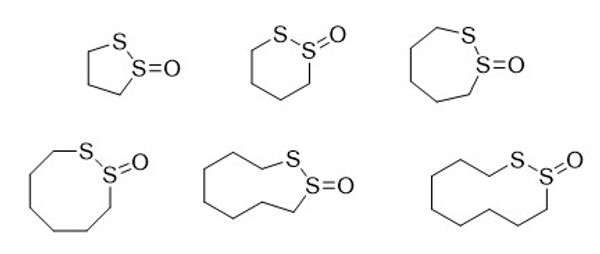
Our current efforts seek to explore novel chemical space of cyclic thiosulfinates using both new and well-established chemistry for unique purposes. These novel cross-linkers aim to provide the basis of an SAR profile of the many cross-link targets and allow for a medicinal chemistry optimization approach as well as to facilitate MS-based identification of the cellular targets of cyclic thiosulfinates.
Photoaffinity Labeling
Photoaffinity labeling is a biochemical technique used for determining behavior of biomolecules. A photoaffinity labeled ligand and a target of interest are covalently crosslinked in response to a specific wavelength of light. 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirines, one common photoaffinity label, are not stable in ambient light and have low aqueous solubility, limiting their utility in biologically relevant environments.
Our group has shown that the addition of heteroaromatic character on diazirine labels improves their ambient light stability and solubility. These promising initial improvements have allowed our group to maintain interest in the synthesis of future generations of diazirine photoaffinity labels with further improved physicochemical properties.
Selected Publications
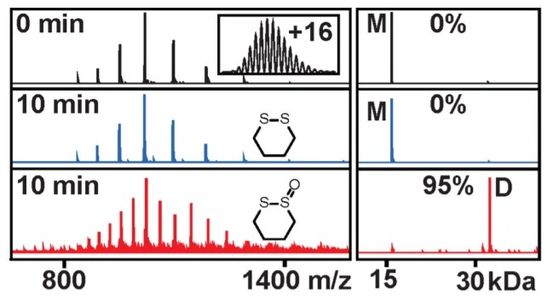
Donnelly, D P; Dowgiallo, M G; Salisbury, J P; Krishna, C; Iyengar, S; Chaudhari, M; Mathew, M; Miele, I; Auclair, J R; Lopez, S A, Manetsch R, Agar J N. J Am Chem Soc 2018; 140, 7377–7380.
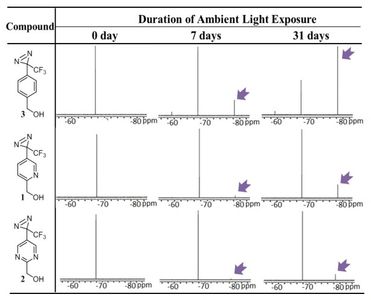
3-Trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirine Photolabels with Enhanced Ambient Light Stability.
Kumar A B, Tipton J D, Manetsch R. Chem Commun 2016; 52, 2729-2732.
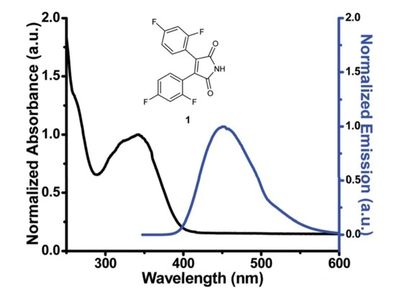
Fluorescent Properties and Resonance Energy Transfer of 3,4-Bis(2,4-difluorophenyl)-maleimide.
Nacheva K P, Maza W A, Myers D Z, Fronczek F R, Larsen R W, Manetsch R. Org Biomol Chem 2012; 10, 7840-7846.

Design, synthesis and photoactivation studies of fluorous photolabels.
Kumar, A. B.; Anderson, J. M.; Manetsch, R. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 6284–6292.